On this page you will see a list of iconophonics divided into plosives, fricatives, percussives, stops, vocals, and effectors. Iconophonics describe how sounds are made by the interactions of mouth parts. They also show how sounds are shaped. Iconophonics are combined to make more complex sounds.
For a more detailed explanation, read this introduction to phonics and the overview of beatboxology.
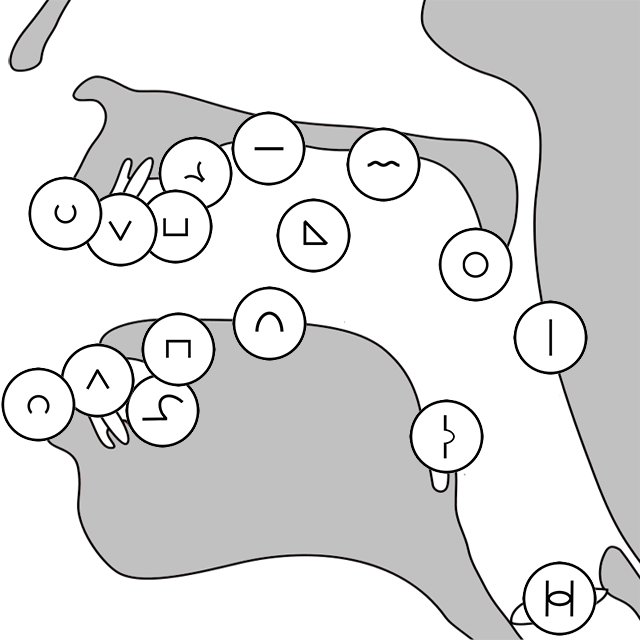
Plosives are indicated by the two mouth parts touching.
Fricatives are indicated by the two mouth parts not touching.
Fricatives are indicated with a small circle overlapping the two mouth parts.
Stops are indicated by the two mouth parts being connected by a line.
Effectors shape the sound.
Vocals can be high, mid, or low pitched.
BZZKTT Version 8.2 • © 2015-2020 Gavin ‘Beatbox’ Tyte (aka TyTe) • All Rights Reserved
BZZKTT is kindly hosted by Alex Tearse from Reefnet.
Special thanks to Alex Tearse, Paul Arnett, Michael Wyatt, Tyler Thompson, Helen Tyte, David ‘Goznet’ Gosnell, and Jerusalem Productions.